- Knowledge Base
- Setup Guides
- How to ping servers and see if they are alive

Servers can be website servers, server at your office or server/nas at your home.
The best way to see if your server is alive is to Ping / ICMP:
The Ping utility is essentially a system administrator’s tool that is used to see if a computer is operating and also to see if network connections are intact. Ping uses the Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Echo function which is detailed in RFC 792. A small packet is sent through the network to a particular IP address. This packet contains 64 bytes – 56 data bytes and 8 bytes of protocol reader information. The computer that sent the packet then waits (or ‘listens’) for a return packet. If the connections are good and the target computer is up, a good return packet will be received. PING can also tell the user the number of hops that lie between two computers and the amount of time it takes for a packet to make the complete trip. Additionally, an administrator can use Ping to test out name resolution. If the packet bounces back when sent to the IP address but not when sent to the name, then the system is having a problem matching the name to the IP address. As mentioned previously, Ping has also evolved from a noun/acronym into a verb, for example: “Ping server X to see if it is up” The time it takes for the packet to get to the target computer and back again is known as the round trip time. If this takes an extended period of time, it is indicative that something may be wrong.
How to use Ping
You can use Ping to perform several useful network diagnostics, such as the following:
- Access – You can use Ping to see if you can reach another computer. If you can’t ping a site at all, but you can ping other sites, then it’s a pretty good sign that your network is fine and that site is down.
- Time & distance – You can use Ping to determine how long it takes to bounce a packet off of another site, which tells you its distance in network terms. For example, a site hosted on your neighbour’s computer next door with a different Internet service provider might go through more routers and be farther away in network distance than a site on the other side of the ocean with a direct connection to the Internet backbone. If a site seems slow, you can compare ping distances to other sites to determine whether it is the site, the network, or your system that is slow. You can also compare ping times to get an idea of which sites have the fastest network access and would be most efficient for downloading, chat, and other applications. We offer you multiple locations around the globe to ping your servers.
- Domain IP address – You can ping either a domain name or an IP address. Pinging both of them and comparing results on possible alert will help you diagnosing problem faster.
Our pings are sent from multiple locations which you can choose, not from your computer, so the times returned reflect the time for communication from ping location, not from your computer. However, they are useful to determine if an address can be reached from different places around the Internet, and to determine how long it takes to reach one site compared to others from most sites.
If the times returned by several web ping sites to a given site are long, then the site’s network is likely having problems. If you can ping a site from our ping locations site but not from your own computer, then there is some block in your network preventing you from reaching that site.
When you are adding or editing your Monitor, click on Advanced Settings.
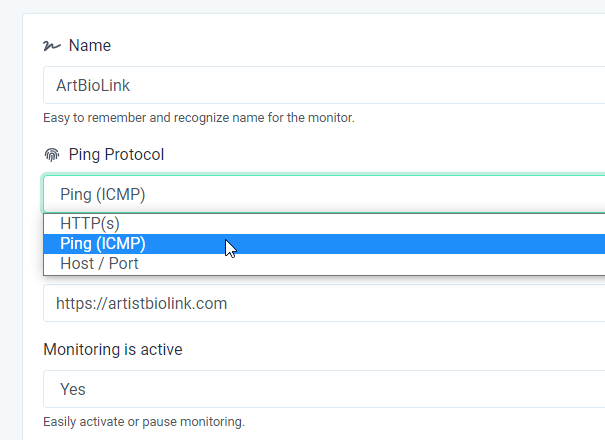
Choose Ping (ICMP) to see if servers are alive as this is the best method for checking server availability.
